Sezaki & Nishiyama Laboratory
Institute of Industrial Science / Center for Spatial Information Science in The University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science / Center for Spatial Information Science in The University of Tokyo
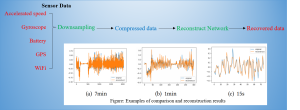
As intelligent sensing and smartphone technologies have progressed, companies collect smartphone data from the app and upload it to servers to provide better daily services. Over time, a large amount of data has been accumulated, placing a heavy burden on the storage of smartphones and servers. Data compression is one strategy to solve this problem.Compressed sensing is one data compression method that significantly reduces compression time compared to traditional methods. However, traditional compression sensing methods are time-consuming and have limited reconstruction performance.
(more…)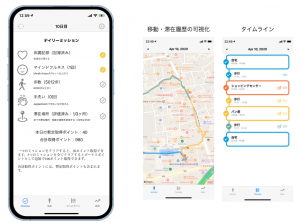
Under the circumstance of the rapid spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, enhancing human’s awareness of self-protection is one practical method to slow down the epidemic. In this study, we utilize mobile sensing to track human activity and guide human’s epidemic prevention behavior by gamified feedback techniques by our developed application SelfGuard. Virtually, human’s self-protection awareness is affected by many factors and the measures to enhance people’s self-protection behavior against the epidemic COVID-19 has always been an unresolved issue. In order to search for factors that influence human’s self-protection behavior, we analyzed the relationships between various human activities and the percentage complete of human’s self-protection behavior and we have extracted some more general conclusions from the results.
(more…)
MOCHAは、東京大学発の接触確認・混雑度確認を目的とした教室等予約・情報提供サービスです。ウィズコロナにおける安心できるキャンパスライフ実現のための位置情報サービス基盤として開発・運用されています。MOCHAは各部屋に設置されたBluetoothビーコンをスマートフォンを用いて検出することで、自動的に滞在場所を記録します。また、事前に設定した共有範囲・粒度で滞在情報を共有することで、キャンパス内における様々な位置情報サービスを開発しています。現在、6500名以上がアプリケーションを利用し、Bluetoothビーコンは2000カ所以上に設置されています。
(more…)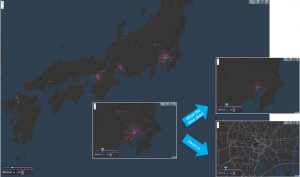
近年は,都市交通計画や感染症対策など,様々な分野で人の流れを把握することが重要となっている.しかし,人の流れを把握する手法の多くは都市部に限定されており,擬似的な人流データを用いて全国規模で行われた研究は少ないのが現状である.一方で,データの可視化にベクトルタイル技術を用い,ズームレベルに応じてデータの粒度を変えることで,データ量の削減や処理速度の向上が期待できる.そこで,全国規模約1億2千万人を対象とした擬似人流データについてベクトルタイル技術を用い,ズームレベルに応じて道路属性を選択することで効率的な可視化を図った結果,データ量は約57%に削減され,タイムスライダーやズームレベルを変化させてもスムーズに可視化を行うことが可能となった.
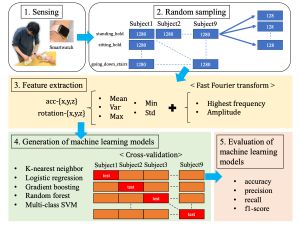
女性の社会進出や核家族化,産後うつ問題など,子育て環境は大きく変化しており,子育ての効率化や子育て支援は社会的に大きな課題となっている.本研究では,近年普及傾向にあるウェアラブルデバイスを用いて,ミルクやオムツ替え,お散歩など「親」が「乳幼児」に行う子育て行動の検知技術の開発を行う.子育て中のモーションデータを腕時計型のウェアラブルデバイスに搭載されたモーションセンサを用いて収集し,収集データと機械学習を用いて子育て行動の検知モデルを構築する.9つの子育て行動を定義し,子育て行動の検知モデルの構築とその精度評価を行った結果,実験室環境において9名の被験者から収集したデータセットを用いた検知モデルでは,最も精度の良いモデルで約70%の精度で子育て行動を検出できることが明らかになった.
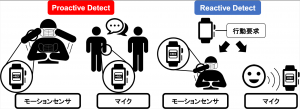
新型コロナウィルスの世界的蔓延により,感染拡大を予防するためにマスクの装着などの飛沫感染リスクを下げる行動が求められる.
感染リスクを低下させるためには,常時マスクを装着することが望ましいが,無意識のうちにマスク非装着のまま行動してしまうことがしばしば発生する.マスク装着を校歌的に促すためには個々人のマスク装着状態を自動検知して,その状態に応じてユーザに対する行動変容を促すことが求められる.しかし,マスク装着状態を市販の端末のみで常時検知する手法は提案されていない.そこで,スマートウォッチに搭載されている複数のセンサを用いてマスク装着状態を自動検知し,マスク非装着のユーザに通知することで,マスク装着の行動を促進させる手法を提案した.

Head movement for traffic visual searching, is one of the important factors in traffic safety. In this paper, we present the design, implementation, and preliminary evaluation of the HeadSense, a helmet device that detects the head movement of micro-mobility rider. HeadSense is capable of generating data streams using the embedded 9-axis inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensor. After the process of segmentation and classification algorithm, HeadSense can automatically detect an individual’s head movement sequence and visual search episodes, across the rider’s entire riding journey. Experiments with 5 participants show that our system achieves 94.7% for per-second level detection and 80.59% F1-score for per-episode level detection.

The use of micro-mobility (e.g., bicycle and scooter) and their data for urban sensing and rider assessment is becoming increasingly popular in research. However, different research topics require different sensor setups; no general data collecting tools for the micro-mobility makes the researcher who wishes to collect data has to build their own collecting system from scratch. To this end, we present MiMoSense, an open crowdsensing platform for micro-mobility. MiMoSense consists of two components: (1) MiMoSense server, which is set up on the cloud, and used to manage sensing studies and the collected data for research and sharing. (2) MiMoSense client, uses micro-mobility carrying various sensors and IoT devices to collect multiple kinds of data during traveling. As a reusable open-source software, MiMoSense shifts the researcher’s focus from software development to sensing data analysis; it can help researchers quickly develop an extensible platform for collecting micro-mobility’s raw sensing data and inferring traveling context. We have evaluated MiMoSense’s battery consumption, message latency and discuss its use.
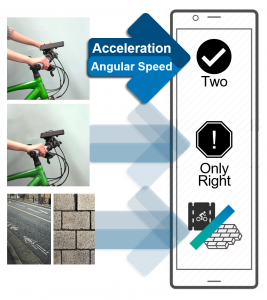
Riding bikes with only one hand on the handlebar can severely undermine the steering capability of riders and risk road safety. In this study, we propose a first detection framework for monitoring single-hand cycling on bicycle travel, called DoubleCheck. It is based on the premise that riders adapt their body movement during single-hand cycling, which is distinguishable to the sensors even amid noise from the exasperate road surface. The system can detect handlebar holding under different road conditions using motion signals from a built-in inertial measurement unit (IMU) in a handlebar mounted smartphone. We implemented the system and invited 10 participants for our evaluation experiment. Our results show that DoubleCheck achieved an F1-score of 0.94 for hand detection, proving its efficacy for real-life implementation to improve road safety.
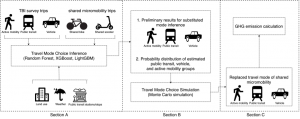
Shared micromobility is widely recognized as an environmentally friendly travel mode and a critical component of transportation decarbonization. However, quantitatively assessing its environmental impact using real-world trip data is an unresolved and challenging subject. To this end, we proposed a system combining machine learning algorithms and Monte Carlo simulation to address this issue. First, several machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, XGBoost, and LightGBM) were utilized to identify citizens’ travel mode choice preferences and then estimate the substituted travel mode of each micromobility trip. Second, to ensure the reliability of the final environmental impact assessment, the Monte Carlo simulations were used to simulate the substituted mode of each trip. Finally, the environmental impacts were calculated based on the life cycle greenhouse gas emissions.
(more…)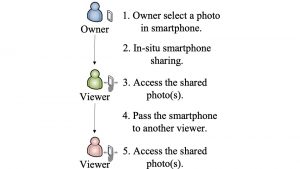
People nowadays are getting used to using mobile phones for daily photography, and sharing these precious moments online or in-situ with their friends. However, there is a potential risk of privacy leakage during the in-situ photo sharing process. To address this risk, we propose OASIS, a cOntext Aware photo protection for in-SItu sharing behavior: using the front camera to tell different viewer, OASIS customize viewer’s photo gallery seamlessly between different viewers according to the context of the photo. In this way, we can provide viewers with a good sharing experience while protecting the privacy of the owner.

Modern mobile applications have become computationally intensive as recent developments in machine learning and computer vision have instigated a new consumer trend for virtual applications. Most of the heavy lifting is traditionally offloaded to cloud servers; however, network latency hinders user experience, making real-time rendering implausible for sophisticated applications. Although mobile devices are capable of performing necessary real-time calculations, mobile devices typically cannot sustain heavy workloads. Edge servers become useful in these scenarios as they are powerful and close enough to users to support real-time applications. Computer vision applications are currently being investigated.

People interact frequently with others in their daily life. Mobile phone has become one of essential parts of people’s daily life, data collected from mobile phones have the potential to infer the relational dynamics of individuals. This study addresses the problem of interpre(ng social rela(onships from human – human interactions captured by mobile sensing networks.

Molecular communication (MC) has been widely studied recently, because of its feasibility at Nano-scale and bio-friendly character over conventional communication techniques. Since communication distance is fundamental for reliable connection among other related applications, efficient and robust distance measurement in MC is desired. To this end, we investigate an approach using arrival time difference for diffusion-based molecular communication systems.
(more…)